Market Overview
The National Pension System (NPS) continues to attract attention as a secure, tax-beneficial investment option for long-term retirement planning.
Originally designed for government employees in 2004 and later expanded to all sectors in 2009, the NPS has maintained its appeal by providing retirement income through a disciplined, market-linked approach.
With recent regulatory updates from the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), the NPS now offers extended benefits for senior citizens and greater flexibility post-retirement.
New Flexibility and Senior Citizen Investment Rules
For those nearing or past retirement, the updated NPS rules open up opportunities that didn’t exist before.
Investors between the ages of 60 to 65 can now continue contributing to their NPS accounts until 70. Upon reaching maturity, subscribers must use 40% of the accumulated corpus for annuities, ensuring a lifetime pension, while the remaining 60% can be withdrawn as a lump sum.
Tax Benefits: The NPS offers significant tax exemptions under Sections 80CCD(1), 80CCD(1B), and 80CCD(2) of the Indian Income Tax Act.
Subscribers can claim up to ₹2 lakh in deductions, including an additional ₹50,000 over the standard ₹1.5 lakh deduction under Section 80C.
This flexibility makes NPS a unique offering for retirement. Even with strict withdrawal guidelines, the system encourages disciplined investing, creating a substantial post-retirement income.
Impact on Investors: Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities:
- Low-Cost and Reliable: With one of the lowest cost structures in the market—0.02% annual advisory fees capped at ₹1,000—the NPS remains an affordable investment option. This allows more capital to compound, providing stronger returns over time.
- Guaranteed Annuity Income: The mandatory annuitisation ensures subscribers receive a steady income throughout retirement, a significant advantage for those prioritizing stable income over liquidity.
Challenges:
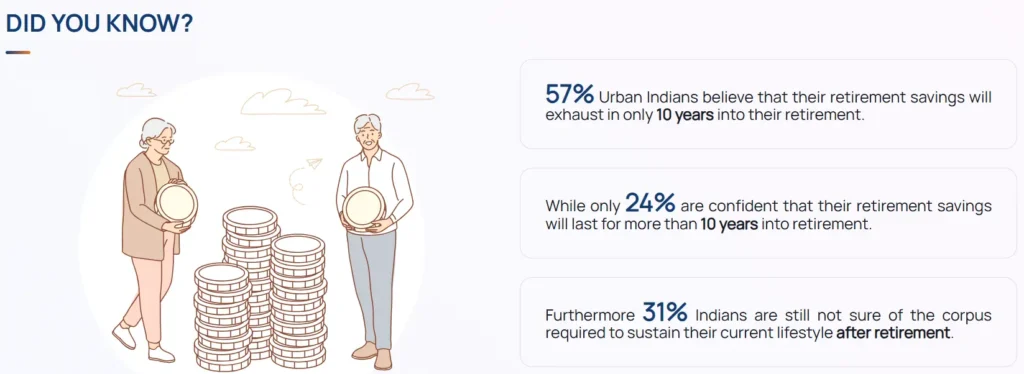
Despite these advantages, the NPS adoption rate remains low, with only 17% of the surveyed population actively investing in it.
According to the IRIS 4.0 study by Max Life Insurance, many investors perceive the scheme as complex and difficult to navigate.
Servicing and communication gaps were other pain points highlighted by dissatisfied users.
“The study found that 53% of people still need guidance on NPS investments, which hinders its potential to become the go-to retirement scheme,” the Max Life Insurance IRIS report.
Future Outlook: Where is NPS Heading?
With the introduction of more flexible policies, the NPS could see increased adoption, particularly among senior citizens and the urban workforce.
However, key hurdles, like complex withdrawal processes and a lack of awareness, need addressing to ensure broader participation.
To bridge this gap, financial institutions could benefit from enhancing advisor incentives to promote NPS more actively, while also simplifying investment processes.
Long-Term Projections:
The NPS offers a balanced approach to retirement planning by encouraging disciplined investment while offering tax-saving opportunities.
If service and user experience improve, the NPS could become a dominant tool for retirement in the Indian market.
Key Takeaways
- Tax Benefits: NPS investments provide multiple avenues for tax savings under Section 80C.
- Income Stability: Mandatory annuity purchase ensures retirees have a stable income source.
- Extended Contributions: Subscribers aged 60 to 65 can continue investing, extending their retirement corpus growth.
Bottom line
The retirement landscape is evolving, with tools like the NPS providing adaptable solutions for different life stages. Stay updated on further changes to maximize your retirement potential.
Sources:- zeebiz[1], informalnewz[2], economictimes[3]
Important links:- www.npscra.nsdl.co.in[1]. IRIS 4.0 – India Retirement Index Study[2].



