India’s stock exchanges, primarily the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE), are vital pillars of its financial sector.
They provide an avenue for investors to build wealth and for companies to raise capital.
With a professional structure and a commitment to regulation through the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), these exchanges promote transparent and fair trading practices.
What is a Stock Exchange and How Does it Work?
The Indian stock exchange acts as a marketplace where shares, bonds, and commodities are bought and sold.
It’s like a large online market where individuals and companies can trade shares of ownership in companies.
When you buy stocks, you’re essentially buying a small part of that company, hoping its value will grow over time.
While this platform enables individuals and businesses to invest and trade, only companies listed on these exchanges can participate in trading.
The electronic order-driven system used by both BSE and NSE ensures a transparent and efficient process where market orders are matched by sophisticated computer algorithms.
How Trades Happen:
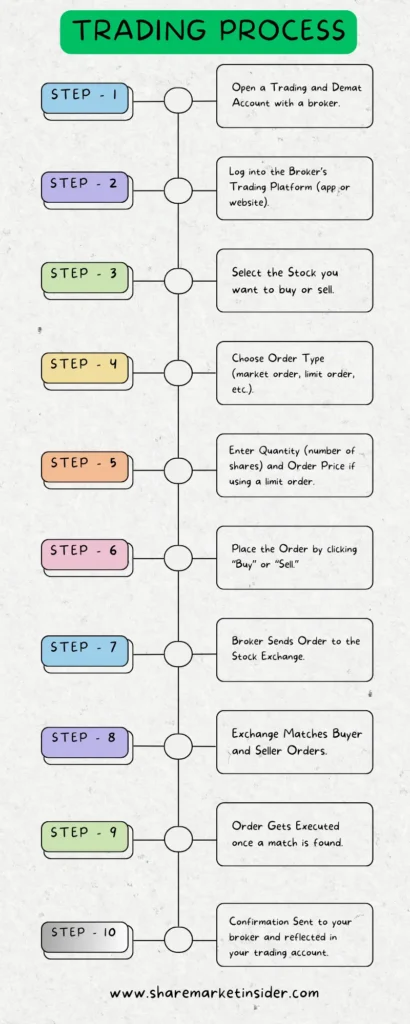
Trades in India are facilitated by brokers who provide retail and institutional investors with access to the stock exchange through Direct Market Access (DMA) systems.
Investors can place orders directly into the trading system using the brokers’ terminals, allowing them greater control and transparency.
Key Benefits of Listing with an Indian Stock Exchange
Listing on a stock exchange gives companies several advantages that enhance their credibility, improve their access to capital, and provide liquidity for shareholders.
- Increased Credibility: Companies listed on prominent exchanges like BSE and NSE are seen as more trustworthy, making their stocks more attractive to potential shareholders.
- Access to Capital: Publicly listed companies can more easily raise capital through share issuance, which helps in financing operations and growth initiatives.
- Liquidity for Investors: Listed shares offer shareholders the advantage of liquidity, allowing them to buy and sell shares with ease and benefit from price changes.
- Fair Price Discovery: Through supply and demand dynamics, prices of listed securities reflect their fair market value, providing investors confidence in the prices they pay.
Here’s a table comparing the benefits of stock listing for both investors and companies:
| Benefit | Investors | Companies |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | Allows investors to easily buy and sell shares | Provides liquidity for existing shareholders |
| Credibility | Enhances trust with a regulated, transparent company | Improves brand reputation and public image |
| Capital Access | Access to diverse investment opportunities | Raises capital for growth, R&D, or expansion |
| Valuation Transparency | Clear stock price reflects market value | Enables transparent valuation for mergers & funding |
| Dividend Potential | Opportunity for income through dividends | Distributes profits to attract and retain investors |
| Portfolio Diversification | Enables risk management across various assets | Attracts a wider investor base |
| Ownership Transferability | Simple process to buy/sell equity | Facilitates smooth ownership transfer |
| Market Research | Increases market insights for informed decisions | Provides market feedback and investor sentiment |
| Employee Incentives | Opportunity for investment in employer’s shares | Offers stock options to attract talent |
Major Stock Exchanges in India: BSE and NSE
India’s two primary stock exchanges play distinct roles in the financial ecosystem, with each serving as a benchmark for the market.
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): Established in 1875, BSE is Asia’s oldest exchange, known for the Sensex, which tracks the performance of 30 leading companies. It is the ‘World’s 6th largest Stock Exchange’ with a market cap of 5.67 trillion USD. source
- National Stock Exchange (NSE): Founded in 1992, NSE introduced electronic trading to Indian markets, a move that enhanced speed and efficiency. NSE’s Nifty 50, which follows the top 50 companies, is a benchmark for Indian investors and global market participants. It is the ‘World’s 7th largest Stock Exchange’ with a market cap of 5.66 trillion USD. source
Both exchanges are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which ensures fair practices and protects investor interests.
Investment Methods:
Investors can access the Indian stock market in two ways: the primary market, where new securities are created, and the secondary market, where existing securities are traded.
- Primary Market: Companies initially offer shares to the public through an IPO (Initial Public Offering). For example, recent IPOs have shown strong performance, signaling investor confidence in India’s growth.
- Secondary Market: Once stocks are listed, they are available on the secondary market, where they can be bought and sold. This market is further divided into the auction market and the dealer market, giving investors different ways to trade.
Emerging Opportunities and Risks in Today’s Stock Exchange Landscape
With India’s rapid economic growth, both domestic and international investors are increasingly drawn to the stock market.
However, it’s crucial to be aware of the opportunities and risks that come with market investments.
- Opportunities in Key Sectors: The technology, pharmaceutical, and renewable energy sectors continue to perform well, driven by innovation and government support. Investing in blue-chip stocks within these sectors might offer stability and steady returns.
- Risks to Consider: Economic shifts like inflation and global market volatility can impact stock values. Investors should also consider the influence of rising interest rates, which may reduce stock market appeal as bond yields become more attractive.
Conclusion:
India’s stock exchange is a powerful gateway to wealth-building and economic growth.
With increasing digital access, market transparency, and government support, the Indian stock exchange is becoming more accessible and investor-friendly.
Also, Read | Beginner’s Guide to Stock Market Investing | नए लोग स्टॉक मार्किट में Invest कैसे करे ?
Also, Read | शेयर बाजार क्या है ? What is the Share market? Share Bazar Basics for Beginners