The Sensex, short for the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) Sensitive Index, isn’t just a number—it’s a reflection of India’s economic vibrancy.
For anyone navigating the world of investments, Sensex is a vital guide. But have you ever wondered why it holds such importance? Let’s understand it.
What Is Sensex?
The Sensex, or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) Sensitive Index, is a flagship benchmark index that reflects the performance of the Indian stock market.
It’s like the heartbeat of India’s economy, capturing the ups and downs of market sentiment. The Sensex tracks the 30 largest and most actively traded companies on the BSE, spanning a diverse range of industries, from banking and IT to energy and pharmaceuticals.
These companies, often called “blue-chip stocks,” are known for their stability, strong financial health, and consistent performance.
Think of them as the reliable stalwarts of the market, representing the cream of Indian enterprise. By aggregating their performance, the Sensex provides a single number that summarizes the overall market’s health and momentum.
Why 30 Companies?
You might wonder—why just 30? Why not 50, 100, or even more? Well, the decision to include 30 companies isn’t arbitrary. It’s a thoughtful balance between breadth and simplicity.
- Diverse Representation: The selected 30 companies span multiple industries, ensuring the index provides a well-rounded picture of the market. From IT giants like Infosys to banking heavyweights like HDFC Bank, each company represents a significant sector of the economy.
- Avoiding Complexity: Including hundreds of companies would make the index overly complicated and harder to interpret. By focusing on 30 major players, the Sensex remains easy to understand, even for non-experts.
- Market Leadership: These 30 companies are often market leaders, influencing not just their industries but also the broader economic landscape.
Think of the Sensex as the “greatest hits” album of Indian businesses. Just as a curated album gives you the best tracks, the Sensex offers a streamlined view of the stock market’s top performers.
It’s comprehensive enough to give you meaningful insights but not so cluttered that it becomes overwhelming.
This curated approach ensures that the Sensex is both practical and powerful, making it a trusted indicator for investors, economists, and policymakers alike.
Also, Read | Stock Market Indices: Understanding the Major Indian Indices
List of BSE Sensex 30 Companies.
Why Does Sensex Matter?
The Sensex is far more than a tool for stock market enthusiasts—it’s a critical indicator of the nation’s economic pulse.
Imagine it as a thermometer for India’s financial health, reflecting the highs and lows of the economy. Here’s why it holds such significance:
1. Economic Trends
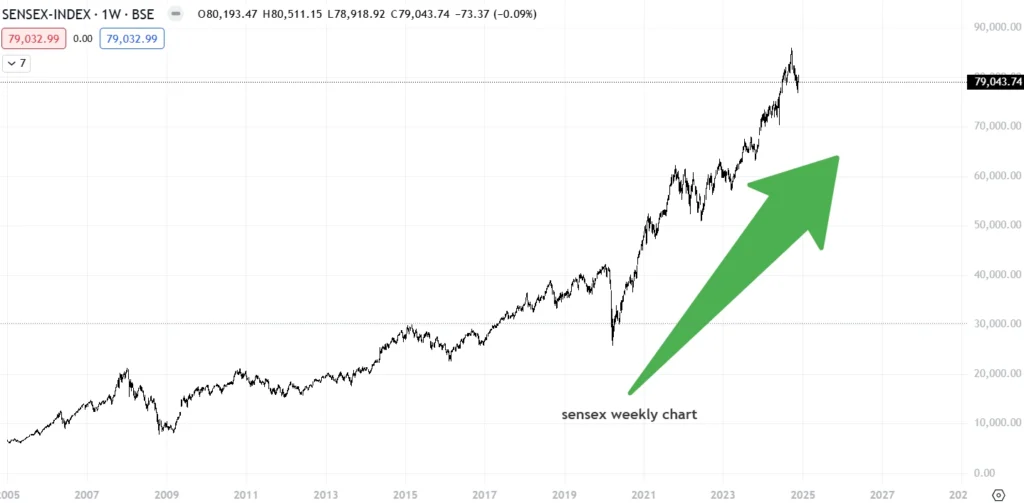
A rising Sensex typically signals optimism about the economy. It means businesses are growing, consumer confidence is strong, and investment flows are robust.
On the flip side, a falling Sensex may point to economic challenges like inflation, policy changes, or global turbulence.
For example, when the Sensex surged past the 60,000 mark in late 2021, it mirrored the post-pandemic recovery, reflecting renewed vigor in various sectors.
Similarly, a decline, such as during the COVID-19 lockdowns, hinted at the economy’s struggles. What does this mean for you? The Sensex helps you understand the big picture.
Whether you’re investing or planning major financial decisions, keeping an eye on economic trends can be invaluable.
2. Investor Sentiment
The Sensex doesn’t just track company performance—it also captures how investors feel about the market. Are they bullish or bearish? Optimistic or cautious?
When the Sensex climbs, it’s often because investors are feeling confident, pouring money into the market.
This confidence could stem from strong corporate earnings, favorable government policies, or global stability.
Conversely, a dip suggests apprehension, driven by fears of inflation, geopolitical tensions, or weak economic indicators.
Why does this matter? Even if you’re not a seasoned investor, understanding market sentiment can help you gauge whether it’s a good time to invest—or hold back.
3. Global Comparisons
The Sensex is not just a domestic barometer; it’s a tool for benchmarking India’s economy on the global stage. Investors around the world look at the Sensex to evaluate India as a market for investment.
Its performance influences foreign portfolio inflows, global fund allocations, and perceptions of India’s growth potential.
For instance:
- A rising Sensex signals that India is on the right track economically, attracting foreign investors.
- Comparisons with indices like the Dow Jones, FTSE, or Nikkei show how India stacks up against other global economies.
How does this help you? Whether you’re a domestic investor or someone keeping tabs on India’s position in the global economy, the Sensex acts as a bridge to the international market narrative.
In a Nutshell: Why Should You Care About the Sensex?
The Sensex is more than just a financial tool—it’s a window into the economy’s past, present, and future.
Whether you’re a business owner, policymaker, or someone planning for the long term, the Sensex is your guide to understanding where India stands and where it’s heading.
After all, when the Sensex moves, it’s not just numbers—it’s a story about growth, challenges, and opportunities.
How Is the Sensex Calculated?
Ever stopped to wonder how the Sensex—those all-important digits flashing on financial screens—is calculated?
It’s not random; it’s based on a precise and widely recognized method called the free-float market capitalization-weighted methodology.
While the term might sound technical, the logic behind it is straightforward. Let’s break it down step by step:
1. What Is Free-Float Market Capitalization?
Free-float market capitalization refers to the total market value of a company’s publicly available shares—those shares that can be traded by investors.
Here’s the key:
- Excluded Shares: Shares held by company promoters, government entities, or those under restrictions are excluded. Why? Because these shares aren’t available for regular trading and don’t affect daily market dynamics.
- Included Shares: Only shares freely available in the market, which reflect the true trading potential of the company, are considered.
By focusing on a free-float market cap, the Sensex ensures a more accurate representation of market sentiment, as it reflects what’s actually in play on the trading floor.
2. Weighting by Size
In the Sensex calculation, larger companies have a bigger influence on the index. Why? Because their market cap (the total value of their free-floating shares) is much higher, meaning they represent a significant portion of the market.
Here’s an example:
- If a banking giant like HDFC Bank performs exceptionally well, its larger market cap means it will push the Sensex higher than a smaller company from the same index.
- Conversely, if a smaller company faces a downturn, its impact on the Sensex will be much less pronounced.
This weighted approach ensures that Sensex reflects the real impact of market leaders while still capturing the collective trends of all 30 companies.
3. The Formula
If you’re into math, here’s the simplified version of how it works:

The index divisor is a standardized figure used to maintain continuity in the Sensex even when companies are added or removed. It ensures the index remains comparable over time.
Why This Methodology Matters
The free-float market capitalization-weighted system ensures that the Sensex stays relevant, adaptable, and reflective of real-world market dynamics.
- Dynamic Adjustments: If a company grows, splits shares, or issues new equity, its free-float market cap is updated, and so is its weight in the Sensex.
- Focus on Liquidity: By excluding non-tradable shares, the Sensex emphasizes what truly matters to active investors.
Real-Life Takeaway
Think of it this way: the Sensex acts like a well-balanced recipe. Each company contributes its unique flavor (market cap), but the most significant ingredients (the largest companies) define the overall taste. This ensures the index is a reliable reflection of the market’s overall health.
So the next time you see the Sensex rise or fall, you’ll know—it’s not magic. It’s math, meticulously tracking the movers and shakers of India’s economy.
What Drives Sensex Up or Down?
If you’ve ever wondered why the Sensex sometimes behaves like a yo-yo—soaring to new heights one day and crashing the next—you’re not alone.
Several factors influence these movements, ranging from domestic developments to global trends. Let’s break them down.
Economic Data: The Big Picture
The Sensex is closely tied to the health of the economy. Positive economic indicators, such as GDP growth, rising employment rates, or strong industrial production numbers, typically boost investor confidence and drive the index upward.
For example:
- If the GDP growth rate exceeds expectations, it signals that businesses are thriving, consumers are spending, and the economy is expanding. This often leads to a surge in stock prices, lifting the Sensex.
- On the other hand, weak economic data—such as high unemployment or declining industrial output—can create jitters in the market, pushing the Sensex down.
Global Markets: A Ripple Effect
The Sensex doesn’t operate in a bubble. In today’s interconnected world, events in global markets can have a direct impact on Indian stocks.
Here’s how:
- Positive Influence: A rally in major indices like the Dow Jones (U.S.), FTSE (U.K.), or Nikkei (Japan) often boosts investor optimism in India, encouraging buying activity and pushing the Sensex higher.
- Negative Influence: Conversely, geopolitical tensions, trade wars, or crises like a global recession can trigger a sell-off in global markets, including the Sensex.
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the collapse of global markets caused the Sensex to plummet by over 50%.
Corporate Earnings: The Scorecard
The performance of the 30 companies in the Sensex plays a pivotal role in its movement. These quarterly results act as a “report card” for the market.
- Strong Earnings: When major companies post better-than-expected profits, it boosts investor sentiment, leading to a rise in stock prices and the Sensex.
- Weak Earnings: Conversely, disappointing results can drag the index down, especially if the underperforming companies hold significant weight in the index.
For example, if IT heavyweights like TCS or Infosys report stellar growth, their positive momentum can lift the Sensex significantly.
Monetary Policies: RBI’s Role
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has a profound influence on the Sensex through its monetary policies, especially changes in interest rates.
Here’s why it matters:
- Lower Interest Rates: When the RBI reduces rates, borrowing becomes cheaper for businesses and individuals, encouraging spending and investment. This can drive stock prices higher, boosting the Sensex.
- Higher Interest Rates: Conversely, rate hikes make borrowing costlier, potentially slowing down economic activity and dampening investor sentiment, causing the Sensex to dip.
For instance, the RBI’s rate cuts during the pandemic helped inject liquidity into the market, driving a recovery in the Sensex.
The Emotional Driver: Investor Sentiment
Let’s not forget the psychological aspect. The Sensex is often driven by fear and greed:
- Optimism: Positive news—whether it’s a reform, a trade deal, or an economic recovery—can lead to a buying frenzy, pushing the Sensex up.
- Pessimism: Negative developments—like a political scandal or a natural disaster—can trigger panic selling, dragging the index down.
The Sensex moves like a finely tuned instrument, responding to a mix of economic realities, corporate performance, and global influences.
By understanding these drivers, you can make sense of their fluctuations—and maybe even use them to your advantage.
So the next time you see the Sensex climbing or dipping, ask yourself: Is it because of new economic data?
A big corporate announcement? Or perhaps something happening halfway across the world? Chances are, it’s all connected.
Is Sensex the Same as Nifty?
Great question! While both the Sensex and Nifty are prominent stock market indices in India, they are not the same.
Think of them as two sides of the same coin—both serve as barometers of the stock market but are designed with slightly different scopes and characteristics. Let’s break it down.
The Basics
- Sensex:
- Tracks 30 companies listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
- Focuses on the largest and most actively traded stocks on the BSE, offering a concise snapshot of the market.
- Nifty 50:
- Tracks 50 companies listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
- Covers a broader selection of companies, representing an expanded view of the market.
Both indices select companies based on factors like market capitalization, liquidity, and sectoral representation, ensuring they reflect the performance of key industries.
Market Coverage
While the Sensex provides insights into the BSE, the Nifty focuses on the NSE, India’s largest stock exchange by trading volume. Together, they complement each other, offering a comprehensive picture of the Indian stock market.
- Sensex: Ideal for those who prefer a more focused look at market leaders.
- Nifty: Provides a slightly broader perspective, given its inclusion of 50 companies.
Performance Comparison
Interestingly, the performance of the Sensex and Nifty often aligns because they both track large-cap companies. However, the differences in their composition and calculation methods can lead to slight variations.
For example:
- If a company is part of the Nifty but not the Sensex (since it tracks 20 more companies), and it performs exceptionally well, the Nifty might outperform the Sensex in percentage growth.
Which One Should You Follow?
It depends on your investment goals:
- Casual Observer: If you’re just trying to gauge the overall market sentiment, following either index will give you a good sense of trends.
- Active Investor: Consider both, as each index highlights slightly different market dynamics.
Both are essential tools for investors, offering insights into India’s financial markets from two unique angles. So, whether you prefer the “30” or the “50,” rest assured—you’re looking at the pulse of the Indian economy.
Also, Read | Nifty50 Simplified: A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investing
Final Thoughts
The Sensex isn’t just a stock market index; it’s a reflection of India’s economic journey, a barometer that captures the nation’s growth, challenges, and aspirations.
Over the decades, it has witnessed—and mirrored—India’s transformation from an emerging market to a global economic force.
For investors, it’s more than just a number; it’s a guide to understanding market trends, economic cycles, and business dynamics.
Even if you’re not an active trader, the Sensex offers valuable insights into the health of the economy and the opportunities it holds.
So, the next time you see the Sensex in the news or hear someone discussing its latest movements, take a closer look.
It’s not just a string of digits—it’s a story. A story of businesses, innovation, resilience, and the ever-evolving spirit of India.
Have you ever used the Sensex to guide your investment decisions? Or perhaps you’ve noticed how it impacts the economy at large?
Share your experience in the comments below—we’d love to hear your story!
Also, Read | Understanding the Indian Stock Exchange