What is Future Trading?
Future trading is a kind of contractual agreement known as future contracts. These agreements bind parties to buy or sell assets at predetermined prices on specified future dates.

It’s like making a deal today for something you’ll receive or deliver on or before the expiry date. This can include stocks, commodities like gold or oil, financial instruments, or even agricultural products.
Participants in these markets include investors, hedgers, and speculators.
Understanding the Basics of Future Trading:
In future trading, we have to trade with future contracts that are a type of derivative.
‘Derivatives’, as the name suggests, is a type of contract whose value is derived from another financial asset known as an ‘Underlying Asset’.
Examples of The underlying assets are stocks, bonds, commodities, currency, etc.
Future Trading Example:
Suppose Reliance is currently trading at 2300 and you have analyzed that in the future Reliance’s value is going to increase, then you can choose to buy Reliance future (suppose Reliace Nov Fut, which is Reliance future contract of November month.)
Now, you will think why buy future contracts and not directly the Reliance stock?
The lot size for Reliace is 250 and if you buy 250 stocks of Reliance shares directly then you have to pay 5,75,000/- but in case of a future contract you can buy 1 lot (250 stocks) in just 1,15,000/- only. Future contracts give you 5x leverage.
Another benefit of trading in future contracts is that you can do sell trade in future contracts on a positional basis which you can not do with stocks directly. In stocks, you can do sell trade only in intraday.
Why Trade Futures?
If your analysis tells that in the future date, the price of any financial instrument may increase or decrease, you may want to buy or sell that particular financial instrument in advance to receive potential benefits.
Future trading allows you to go short on the future price movements of assets, providing potential profits even in a declining market.
Contracts and Expiry Dates:
In future trading, you deal with contracts. These contracts have expiry dates, indicating when the agreement must be fulfilled.
So before planning your trades keep in mind the expiry date to avoid any penalties.
Generally, all future contracts in India expire on the last Thursday of each month.
If Thursday happens to be a holiday, then the previous working day of the month is the expiry day.
Unlike option contracts which expire worthless at the end of the expiry day even without exercising. In future contracts, the trader must square off their trading position on or before the expiry date to avoid penalties.
Derivative contract settlements can be done in two ways:
- Cash settlement.
- Physical delivery.
Cash settlement:
This way both parties settle their deal in money or cash instead of actual assets.
Physical delivery:
This mostly happens in commodities where one has to buy that commodity if it is not settled before the expiration.
Note - BANKNIFTY futures contracts expire on the last Wednesday of the expiry month. If the last Wednesday is a trading holiday, the contracts expire on the previous trading day. source
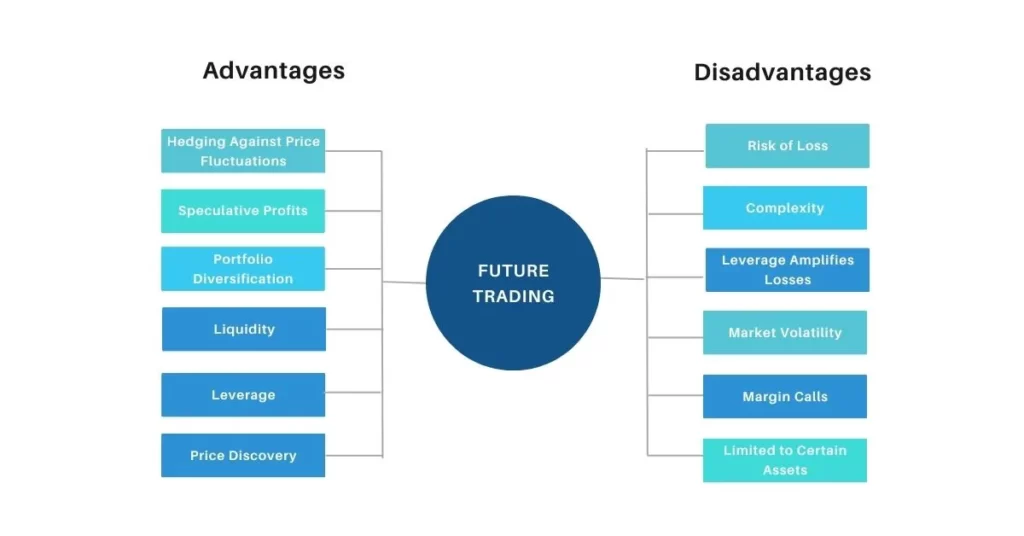
Advantages of Future Trading:
Hedging Against Price Fluctuations:
Future trading allows businesses to hedge against the volatility of commodity prices, ensuring more predictable costs for production.
Speculative Profits:
Traders can profit from anticipated future price movements, even if the market is declining, by buying or selling futures contracts.
Portfolio Diversification:
Including futures in an investment portfolio can provide diversification, spreading risk across different asset classes.
Liquidity:
Many futures markets are highly liquid, allowing for easy entry and exit from trades without significant price impact.
Leverage:
Futures contracts often require a fraction of the total contract value as a margin, allowing traders to control larger positions with a relatively smaller investment.
Price Discovery:
Future markets contribute to price discovery by reflecting the collective expectations and opinions of market participants, providing valuable information to businesses and investors.
Disadvantages of Future Trading:
Risk of Loss:
Futures trading involves a high level of risk, and traders can incur substantial losses if the market moves against their positions.
Complexity:
Understanding the intricacies of futures trading requires a learning curve, and the complexity of the market may be a barrier for some investors.
Leverage Amplifies Losses:
Leverage works both ways While it is used to increase profits, it can also increase the potential losses. Not using it properly can lead to significant financial setbacks.
Market Volatility:
Futures markets can be highly volatile, making it challenging to predict and navigate price movements accurately.
Margin Calls:
If the market moves against a trader, they may be required to deposit additional funds to meet margin calls, leading to additional financial pressure.
Limited to Certain Assets:
Futures trading is primarily focused on specific assets like limited stocks, commodities, financial instruments, or indices, limiting the range of investment options compared to other markets.
Basic terminology of futures trading:
Here’s a table outlining some basic terminology and its definitions of future trading:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Underlying Asset | The financial instrument or commodity on which a futures contract is based. It’s the actual asset that the contract represents the right to buy or sell. |
| Future Contract | An agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of an asset at a predetermined price and future date. |
| Long Position | Buying a future contract with the expectation that the asset’s price will rise. |
| Short Position | Selling a future contract with the anticipation that the asset’s price will decline. |
| Expiration Date | The date on which a future contract expires. All contractual obligations must be fulfilled by this date. |
| Settlement Price | The use of borrowed funds increases the size of a trading position, amplifying both potential gains and losses. |
| Margin | The amount of money or collateral required to open a future position. Acts as a security deposit. |
| Leverage | The total number of outstanding futures contracts in the market, provides insight into market activity. |
| Hedging | The total number of outstanding futures contracts in the market provides insight into market activity. |
| Speculation | The total number of outstanding futures contracts in the market provides insight into market activity. |
| Contract/Lot Size | The amount of the underlying asset fixed for one futures contract. |
| Tick Size | The smallest price movement allowed for a particular future contract. |
| Open Interest | Using future contracts to protect against potential price movements, reduces the risk of financial loss. |
| Market Order | An order to buy or sell a futures contract at the current market price. |
| Limit Order | An order to buy or sell a futures contract at a specific price or better. |
| Stop Order | An order to buy or sell a futures contract once the market reaches a specified price. |
| Contango | A market condition where future prices are higher than the spot price. |
| Backwardation | A market condition where future prices are lower than the spot price. |
Conclusion:
Future trading is a type of trading based on future expectations. It is done through a futures contract or a derivative of the underlying asset.
Remember that all future contracts expire on the last Thursday of each month, and unlike option contracts, traders are obligated to square off their trade position before expiry to avoid any penalties. Settlement can be done in either cash or physical delivery.
FAQs: Future Trading
What is future trading and how does it work?
Future trading involves making agreements to buy or sell assets at a set price on a future date. It works by speculating on the future price movements of assets, offering potential profits even in a declining market.
Is future trading haram?
Future trading is considered haram (prohibited) by some Islamic scholars due to its involvement in riba (usury), gharar (uncertainty), and maisir (gambling).
However, other scholars argue that future trading is permissible under certain conditions, such as when the underlying asset is a legitimate commodity, the delivery of the asset is intended, and the price is determined fairly.
Muslims should consult with a qualified Islamic scholar to determine the permissibility of a specific future trading contract.
Is future trading profitable?
Future trading can be profitable, but it comes with risks. Success depends on market knowledge, strategy, and risk management. Understanding the market dynamics and preparing for potential losses is important.
Is future trading a good career?
Yes, future trading can be a good career option. Whether future trading is a good career choice depends on individual preferences, risk tolerance, and dedication to learning. Successful trading requires continuous education, discipline, and adapting to market changes. It can be a rewarding career for those who are well-prepared and committed.


