In the ever-evolving world of financial markets, traders and investors constantly seek reliable methods to predict price movements and maximize returns. Technical analysis has emerged as one of the most widely used approaches, offering a structured framework for analyzing market behavior based on historical data patterns. Technical analysis looks at price changes and trading volume to predict market trends, while fundamental analysis studies a company’s financial details to find its true value.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll understand not only what technical analysis is but also its significant advantages and disadvantages, enabling you to make informed decisions about incorporating these tools into your trading strategy. With the financial markets becoming increasingly complex, mastering technical analysis has never been more relevant for both novice and experienced traders.
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis is a methodology used to evaluate and predict price movements in financial markets by analyzing statistical trends gathered from trading activity, primarily focusing on price and volume data. Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines economic factors, company performance, and financial statements, technical analysis is based on the premise that all current information is already reflected in the price.
The Core Principles of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis operates on three fundamental principles:
History Tends to Repeat Itself: Market psychology is remarkably predictable, leading to repetitive price patterns. By identifying these patterns, analysts can anticipate future price movements.
The Market Discounts Everything: This principle suggests that all known information—whether financial, political, or psychological—is already reflected in the price. Technical analysts believe they need only study price movements since prices incorporate all relevant market information.
Prices Move in Trends: Technical analysts believe that prices follow trends rather than moving randomly. Once a trend is established, future price movements are more likely to follow that trend than oppose it.
Technical Analysis vs. Fundamental Analysis
When comparing technical and fundamental analysis, it’s important to understand their different approaches and how they can complement each other:
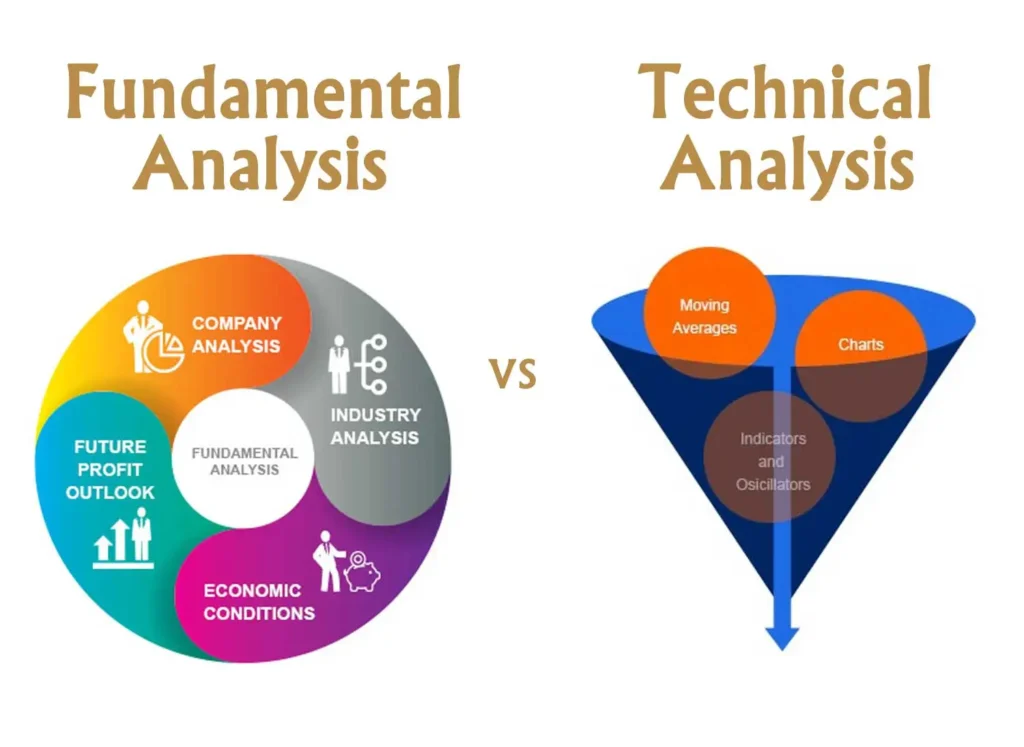
| Aspect | Technical Analysis | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Price movements, patterns, and trading volume | Company financials, industry trends, economic data |
| Time Horizon | Often short to medium-term | Typically medium to long-term |
| Data Used | Historical price and volume charts | Financial statements, economic reports, industry analysis |
| Key Question | “What is happening with the price?” | “Why is the price changing?” |
| Primary Tools | Charts, indicators, trend lines | Financial ratios, growth projections, economic indicators |
| Best Used For | Timing market entries and exits | Determining intrinsic value of securities |
Key Components of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis employs various tools and methods to interpret market data. Here are the essential components:
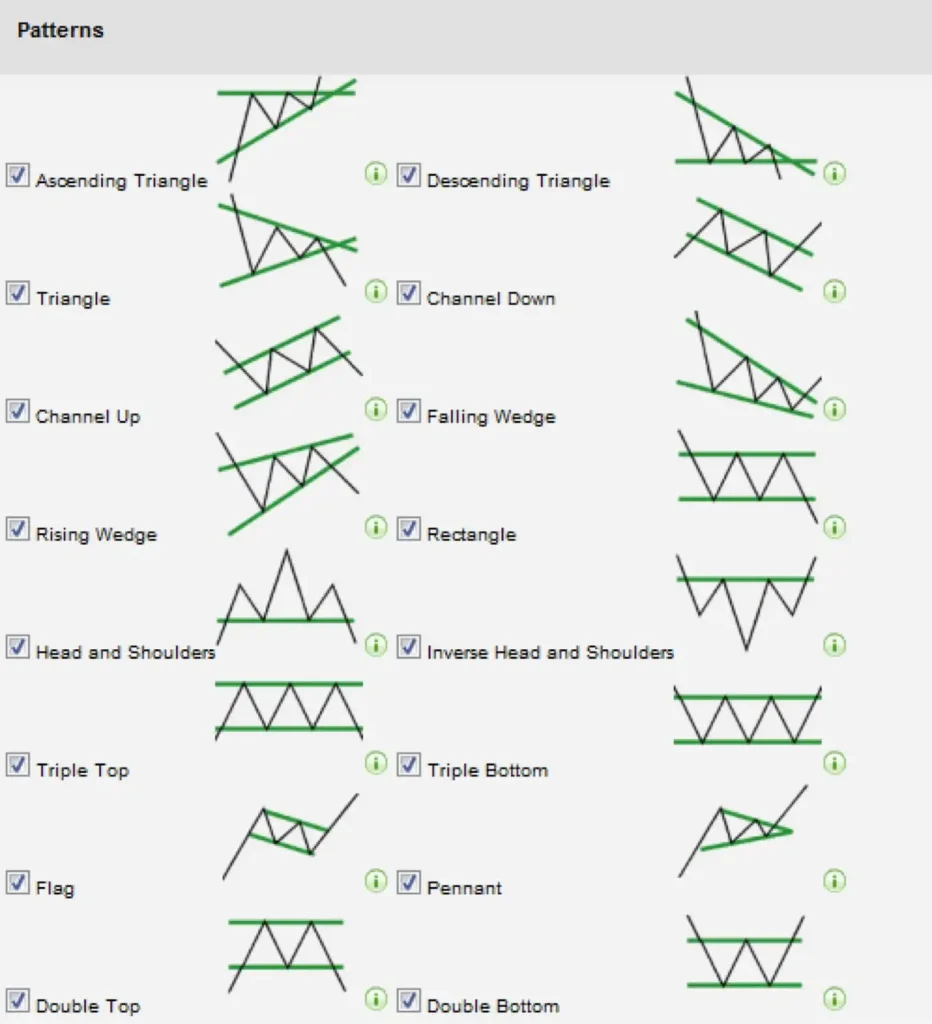
1. Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are specific formations that appear on price charts and signal potential future price movements. They fall into two main categories:
- Continuation Patterns: Indicate that a trend pause will likely be followed by the resumption of the existing trend. Examples include flags, pennants, and triangles.
- Reversal Patterns: It indicates that the market trend might soon reverse, either from rising to falling or vice versa. Examples include head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and rounding patterns.
2. Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are math-based tools that use a security’s price, trading volume, or open interest to help analyze market trends. They help traders identify momentum, trend direction, volatility, and potential reversal points.

Common Technical Indicators and Their Applications
Trend Indicators
- Moving Averages: Smooth out price data to identify trends
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Shows relationship between moving averages
- Average Directional Index (ADX): Measures trend strength
Momentum Indicators
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures speed and magnitude of price movements
- Stochastic Oscillator: Compares closing price to price range
- Commodity Channel Index (CCI): Identifies cyclical trends
Volume Indicators
- On-Balance Volume (OBV): Relates volume to price change
- Volume Profile: Shows trading activity at different price levels
- Accumulation/Distribution Line: Measures money flow into or out of a security
Volatility Indicators
Keltner Channels: Uses average range to plot channels around price
Bollinger Bands: Shows price volatility through standard deviation
Average True Range (ATR): Measures market volatility
3. Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance are price levels where a stock has historically had difficulty falling below (support) or rising above (resistance).
- Support: Price level where buying interest is strong enough to overcome selling pressure
- Resistance: Price level where selling pressure is strong enough to overcome buying interest
- Breakouts: When price moves beyond support or resistance levels, often signaling continued movement in that direction
4. Trend Analysis
Trends represent the general direction in which a security’s price is moving:
- Uptrends: Series of higher highs and higher lows
- Downtrends: Series of lower highs and lower lows
- Sideways/Horizontal Trends: Price moves within a relatively narrow range
Advantages of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis offers numerous benefits to traders and investors looking to make informed decisions in the financial markets.
1. Structured Framework for Decision-Making
Technical analysis provides a systematic approach to evaluating market conditions, helping traders remove emotion from the decision-making process. This structure is particularly valuable during market volatility when emotions can cloud judgment.
According to a 2024 study by the Journal of Behavioral Finance, traders who utilize technical analysis frameworks report 28% lower rates of emotional trading decisions than those who trade based on intuition alone.
2. Versatility Across Markets and Timeframes
One of technical analysis’s greatest strengths is its applicability across different markets and timeframes:
- Market Versatility: Works with stocks, forex, commodities, cryptocurrencies, options, and futures
- Timeframe Flexibility: Can be applied to intraday charts (minutes, hours) as well as longer-term charts (daily, weekly, monthly)
This versatility makes technical analysis a valuable tool for various trading styles, from day trading to position trading.
3. Visual Representation of Market Psychology
Technical analysis provides visual representations of market sentiment through price charts and patterns, making complex market behavior more accessible and interpretable.
“Charts don’t lie. They reflect all known information and the psychology of market participants—fear, greed, hope, and despair—in visual form,” explains Tom DeMark, renowned technical analyst and founder of DeMARK Analytics.
4. Precise Entry and Exit Points
Technical analysis excels at identifying specific price levels for entering and exiting trades:
- Clear Entry Signals: Technical indicators and patterns provide objective entry points
- Defined Exit Strategies: Support for setting profit targets and stop-loss levels
- Risk Management: Helps calculate precise risk-to-reward ratios before entering trades
5. Early Trend Identification
With proper application, technical analysis can help identify emerging trends before they become widely recognized:
- Leading Indicators: Tools like MACD and RSI can signal potential trend changes early
- Pattern Recognition: Chart patterns often form before major price movements
- Divergence Analysis: Spotting discrepancies between price and indicators can forecast reversals
Real-World Example: Early Trend Identification
In January 2024, the S&P 500 showed a bullish divergence between price and RSI – while the index made lower lows, the RSI formed higher lows. Technical analysts who spotted this divergence entered the market before a 15% rally over the next three months, significantly outperforming those who waited for fundamental confirmation of the trend.
6. Objective and Data-Driven Approach
Technical analysis relies on quantifiable data rather than subjective interpretations:
- Quantifiable Parameters: Technical indicators use mathematical formulas with definable parameters
- Backtesting Capability: Strategies can be tested against historical data to validate effectiveness
- Rule-Based Trading: Enables development of systematic trading strategies with clear rules
7. Accessibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Modern technology has made technical analysis accessible to individual traders:
- Free/Low-Cost Tools: Many platforms offer free charting and technical analysis tools
- Educational Resources: Abundant learning materials available online
- Democratization of Finance: Technical analysis levels the playing field between retail and institutional traders
Disadvantages of Technical Analysis
Despite its benefits, technical analysis has significant limitations that traders should understand.
1. Subjective Interpretation
While technical analysis tools provide objective data, the interpretation remains subjective:
- Pattern Ambiguity: The same chart pattern may be interpreted differently by different analysts
- Indicator Selection: Choosing which indicators to use and how to configure them involves subjective judgment
- Confirmation Bias: Traders may see patterns that confirm their existing beliefs
This subjectivity can lead to inconsistent results and varying effectiveness among traders using the same tools.
2. Reliance on Historical Data
Technical analysis assumes that historical price patterns will repeat, which isn’t always true:
- Market Evolution: Markets continuously evolve with new participants, technologies, and regulations
- Black Swan Events: Unexpected major events can invalidate historical patterns
- Limited Sample Size: Some patterns may appear valid but lack sufficient historical occurrences to be statistically significant
“Looking at historical data to predict future movement is like driving by looking only in the rearview mirror,” warns Dr. Burton Malkiel, economist and author of “A Random Walk Down Wall Street.”
3. False Signals and Whipsaws
Technical indicators frequently generate false signals, especially in volatile or ranging markets:
- Whipsaws: Price briefly breaks a technical level before reversing, triggering false signals
- Signal Conflicts: Different indicators often provide contradictory signals
- Overoptimization: Excessive fine-tuning of indicators to fit historical data can lead to poor future performance
A 2023 study published in the Journal of Financial Economics found that approximately 35% of technical breakout signals fail to result in the expected price movement.
4. Lagging Indicators
Many technical indicators are lagging rather than leading:
- Delayed Signals: By the time some indicators generate a signal, a significant portion of the price move may have already occurred
- Trend Confirmation: Many indicators excel at confirming existing trends but struggle to predict new ones
- Moving Average Lag: Popular indicators like moving averages inherently lag price action
5. Ignores Fundamental Factors
Technical analysis focuses solely on price and volume, potentially missing important fundamental developments:
- Earnings Surprises: Cannot account for the impact of unexpected earnings reports
- Economic Data: Doesn’t directly incorporate economic indicators that might affect markets
- Company-Specific News: Ignores developments like management changes, lawsuits, or product innovations
6. Limited Effectiveness in Certain Market Conditions
Technical analysis works best in trending markets but can struggle in other conditions:
- Sideways Markets: Many technical strategies underperform in non-trending, range-bound markets
- Low Liquidity: Less effective in thinly-traded securities where price movements may be erratic
- Highly Manipulated Markets: Vulnerable in markets where large players can influence price action
7. Self-Fulfilling Prophecy Effect
When many traders use the same technical indicators, their collective actions can temporarily create the very patterns they’re following:
- Crowded Trades: Popular technical levels can become overcrowded, leading to sharp reversals
- Diminishing Returns: As more traders adopt a strategy, its effectiveness often decreases
- Algorithm Impact: Automated trading systems may amplify technical-based market moves
Modern Applications and Evolution of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis has evolved significantly with technological advancements and continues to adapt to changing market conditions.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The combination of traditional technical analysis with AI and ML represents a significant evolution in the field:
- Pattern Recognition: Machine learning algorithms can identify complex patterns humans might miss
- Sentiment Analysis: Natural language processing can analyze news and social media to complement technical signals
- Adaptive Indicators: AI can dynamically adjust technical indicators based on changing market conditions
According to a 2024 research paper from the MIT Financial Engineering Laboratory, AI-enhanced technical analysis systems showed a 24% improvement in prediction accuracy compared to traditional technical analysis methods alone.
Breakthrough: AI-Enhanced Technical Analysis
In recent years, sophisticated machine learning models have been developed to enhance traditional technical analysis. These models can:
- Process vast amounts of historical data to identify subtle patterns
- Consider hundreds of technical indicators simultaneously
- Adapt to changing market conditions by reweighting factors
- Reduce false signals by cross-validating patterns across multiple timeframes
The JP Morgan Quantitative Analysis Research team reported in 2024 that their hybrid model combining traditional technical indicators with deep learning achieved 32% higher returns with 18% lower volatility compared to either approach used in isolation.
High-Frequency Trading and Technical Analysis
The rise of high-frequency trading (HFT) has changed how technical analysis is applied:
- Microsecond Timeframes: Technical analysis now extends to ultra-short timeframes
- Order Flow Analysis: Focus on order book dynamics rather than just completed trades
- Statistical Arbitrage: Identifying mathematical relationships between securities
Technical Analysis in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets have embraced technical analysis enthusiastically:
- 24/7 Trading: Continuous markets create more complete technical pictures
- Retail Dominance: High retail participation makes these markets particularly responsive to technical factors
- Volatility Management: Technical tools help manage the extreme volatility characteristic of crypto
“Cryptocurrency markets show particularly strong adherence to technical patterns due to their retail-dominated nature and the absence of traditional fundamental metrics,” notes Willy Woo, on-chain cryptocurrency analyst.
Current Market Data and Technical Analysis
The financial markets present unique challenges and opportunities for technical analysis. Several key trends are worth noting:
Market Volatility and Technical Indicators
Volatility measures have shown interesting patterns:
- The VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) has averaged 19.8 in Q1 2025, compared to 18.3 in Q1 2024
- Bollinger Band width across major indices has increased by 22% year-over-year
- ATR (Average True Range) values have expanded significantly across most asset classes
This increased volatility has implications for technical analysis application, particularly for stop-loss placement and trend identification.
Technical Analysis Success Rates in Current Markets
Recent academic research has provided insights into the effectiveness of various technical strategies:
- A 2024 study by the Journal of Financial Markets found that trend-following strategies based on moving averages delivered positive returns in 68% of tested market environments
- Pattern-based strategies showed more mixed results, with head and shoulders patterns exhibiting a 58% success rate when strict volume confirmation was applied
- Oscillator-based countertrend strategies performed poorly in the current market environment, with only a 42% success rate
Evolution of Technical Analysis Tools
Technical analysis continues to evolve with new tools and methodologies:
- Volume Profile Analysis: Gaining popularity as an advancement over traditional volume indicators
- Machine Learning-Enhanced Indicators: New indicators that incorporate adaptive algorithms
- Market Regime Filters: Tools that identify which technical approaches are most suitable for current market conditions
How to Effectively Apply Technical Analysis
To maximize the benefits while minimizing the drawbacks of technical analysis, consider these best practices:
1. Combine with Fundamental Analysis
Use technical analysis to time entries and exits, but incorporate fundamental analysis to select securities and validate longer-term trends:
- Fundamentally Sound, Technically Timed: Select fundamentally strong securities and use technical analysis for optimal entry/exit points
- Multi-Factor Approach: Consider both technical signals and fundamental data in decision-making
- Timeframe Alignment: Use fundamentals for longer-term direction and technicals for shorter-term timing
2. Use Multiple Timeframes
Analyzing multiple timeframes provides a more complete picture of market conditions:
- Top-Down Analysis: Start with longer timeframes to identify the primary trend, then use shorter timeframes for entry/exit timing
- Timeframe Confirmation: Look for alignment of signals across different timeframes for stronger confirmation
- Fractal Analysis: Understand how patterns repeat across different timeframes
3. Employ Multiple Indicators
Relying on a single indicator often leads to false signals. Instead:
- Confirmation Strategy: Use different types of indicators to confirm signals
- Avoid Redundancy: Choose indicators that measure different aspects of market action
- Prioritize Signals: Develop a framework for resolving conflicting signals
4. Implement Proper Risk Management
Technical analysis should be part of a comprehensive risk management strategy:
- Position Sizing: Calculate position size based on stop-loss placement
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Only take trades with favorable risk-reward ratios
- Portfolio Correlation: Consider how technical signals across holdings might create correlated risks
5. Develop a Trading Plan
Create a structured trading plan that defines:
- Entry Criteria: Specific technical conditions that must be met before entering a trade
- Exit Rules: Predetermined conditions for taking profits or cutting losses
- Trade Management: Guidelines for adjusting positions as market conditions change
Emerging Trends and Future of Technical Analysis
As we look toward the future, several trends are reshaping technical analysis:
1. AI and Big Data Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence and big data is revolutionizing technical analysis:
- Alternative Data: Incorporation of non-traditional data sources like satellite imagery and social media sentiment
- Neural Networks: Advanced pattern recognition beyond traditional technical patterns
- Adaptive Systems: Self-adjusting indicators that evolve with changing market conditions
“The future of technical analysis lies in the intelligent fusion of traditional patterns with artificial intelligence that can process billions of data points simultaneously,” says Dr. Ernest Chan, quantitative trading expert and author of “Quantitative Trading.”
2. Behavioral Finance Integration
Technical analysis is increasingly incorporating insights from behavioral finance:
- Market Psychology Metrics: New indicators specifically designed to measure fear, greed, and other emotions
- Sentiment Analysis: Real-time monitoring of trader sentiment through social media and other channels
- Behavioral Pattern Recognition: Identifying patterns that reflect specific cognitive biases
3. Blockchain and DeFi Applications
Blockchain technology and decentralized finance are opening new frontiers for technical analysis:
- On-Chain Analysis: Technical analysis of blockchain data beyond just price and volume
- Cross-Chain Indicators: Technical tools that analyze relationships between different blockchain networks
- Smart Contract Metrics: Technical evaluation of DeFi protocol usage and liquidity
Case Study: Technical Analysis in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets have proven particularly receptive to technical analysis due to their retail-dominated nature and 24/7 trading. A study by the CryptoCompare Research Division in early 2025 found that:
- Bitcoin exhibited a remarkable 71% adherence rate to classical chart patterns
- Key Fibonacci retracement levels acted as support/resistance with 68% reliability
- Volume-price divergence signals generated an average 24% return over a 30-day period
However, the study also noted that technical signals were frequently invalidated during major fundamental events like regulatory announcements or protocol changes, highlighting the importance of a combined approach.
Interactive Tool Recommendation: Technical Analysis Effectiveness Calculator
I recommend implementing an interactive tool that allows readers to evaluate the potential effectiveness of various technical indicators based on their trading style and market conditions.
This tool would:
- Allow users to select their typical holding period
- Input current market condition parameters
- Choose technical indicators they’re considering
- Receive a compatibility score and suggested configuration
Such a tool would provide personalized guidance on which technical approaches might work best for each reader’s specific situation.
Conclusion: Balancing Technical Analysis in Your Trading Strategy
Technical analysis offers a structured approach to analyzing market behavior and identifying potential trading opportunities. Its advantages—including objectivity, precision in entry/exit points, trend identification, and visual representation of market psychology—make it a valuable tool for many traders.
However, its limitations cannot be ignored. The subjective interpretation of patterns, reliance on historical data, potential for false signals, and disregard for fundamental factors all present significant challenges. Additionally, technical analysis is more effective in certain market conditions than others.
The most effective approach for most traders is to:
- Understand both strengths and weaknesses of technical analysis
- Combine technical and fundamental analysis for a more complete market view
- Use multiple technical tools rather than relying on a single indicator or pattern
- Implement robust risk management regardless of the technical signals
- Continue learning and adapting as markets and technical tools evolve
Technical analysis is neither infallible nor useless—it’s a set of tools that, when used appropriately with proper risk management, can improve trading decisions. The key is developing the knowledge and experience to know which tools to use in which situations, and to maintain realistic expectations about their capabilities and limitations.
As famed technical analyst John Murphy noted, “Technical analysis is the art of identifying trend changes at an early stage and maintaining an investment posture until the weight of evidence indicates that the trend has reversed.” By understanding both its power and its limits, traders can use technical analysis as one important component of a comprehensive trading strategy.
FAQ: Advantages and Disadvantages of Technical Analysis
What is the success rate of technical analysis strategies?
Success rates vary widely based on many factors including the specific technique, market conditions, and trader skill. Recent studies show that common technical patterns like head and shoulders have success rates between 55-65% when properly identified with volume confirmation. Trend-following strategies using moving averages have shown success rates of 60-70% in trending markets but significantly lower rates in ranging markets.
It’s important to note that even a strategy with a 60% success rate can be highly profitable if winners are larger than losers. As Linda Raschke, renowned technical trader, notes: “It’s not about being right all the time—it’s about managing your risk when you’re wrong and maximizing your gains when you’re right.”
How does technical analysis perform in different market conditions?
Technical analysis typically performs best in trending markets where patterns and indicator signals tend to be more reliable. During strong trends, trend-following indicators like moving averages can be particularly effective.
In range-bound or choppy markets, trend-following strategies often struggle with frequent false signals, while oscillators and support/resistance strategies may perform better. During market extremes or black swan events, most technical approaches may fail temporarily as historical patterns break down.
Adapting your technical approach to current market conditions is crucial. As market technician Martin Pring advises, “Different technical tools should be used in different market environments.”
Can technical analysis work with artificial intelligence to improve results?
Yes, this combination is showing promising results. AI and machine learning can enhance technical analysis by:
- Processing vast amounts of data to identify subtle patterns difficult for humans to detect
- Optimizing indicator parameters dynamically based on changing market conditions
- Reducing false signals by assessing multiple confirmatory factors simultaneously
- Identifying which technical approaches are most effective in current market conditions
A 2024 study by QuantResearch found that AI-enhanced technical systems improved prediction accuracy by 22-28% compared to traditional technical methods alone.
Is technical analysis more effective in specific markets or asset classes?
Technical analysis tends to work better in:
- Highly liquid markets with many participants
- Markets with significant retail trader participation (as retail traders often use similar technical approaches)
- Markets where sentiment and psychology play a major role in pricing
Research suggests that technical analysis has shown particular effectiveness in forex markets due to their high liquidity and trend persistence. Cryptocurrency markets have also demonstrated strong adherence to technical patterns, likely due to their retail-dominated nature.
Conversely, technical analysis may be less reliable in:
- Illiquid markets with irregular trading
- Markets heavily dominated by a few institutional players
- Markets where prices are heavily influenced by unpredictable external factors
Should beginners rely on technical analysis for their trading decisions?
Beginners should approach technical analysis with cautious optimism. While it provides a structured framework for decision-making, it also requires significant experience to apply effectively.
New traders should:
- Start with simple, well-established patterns and indicators rather than complex systems
- Focus on risk management first, with technical analysis as a secondary consideration
- Paper trade to gain experience before committing real capital
- Combine technical signals with basic fundamental analysis
- Seek education from reputable sources rather than following “hot tips”
As trading educator Dr. Alexander Elder suggests, “Technical analysis is not a magic formula for success—it’s a skill that requires study, practice, and disciplined application.”
How has technical analysis evolved with modern technology?
Technical analysis has transformed significantly with technological advances:
- Computing power has enabled complex calculations and backtesting that were previously impossible
- AI and machine learning are enhancing pattern recognition capabilities
- Big data analysis allows for incorporation of non-traditional data sources
- Mobile technology enables real-time analysis and alerts
- Social sentiment analysis provides new dimensions to market psychology assessment
Modern technical analysts have access to tools that would have been unimaginable to early practitioners. However, the core principles of examining price and volume patterns to understand market psychology remain fundamentally unchanged.
Does technical analysis work better for short-term or long-term trading?
Technical analysis is generally more effective for short to medium-term trading horizons. In shorter timeframes (intraday to a few weeks), price movements are more influenced by sentiment and technical factors that technical analysis excels at measuring.
For long-term investing (months to years), fundamental factors tend to dominate returns, though technical analysis can still aid with timing entries and exits.
Many successful investors use a blended approach: fundamental analysis for security selection and longer-term outlook, with technical analysis for optimizing entry and exit points.